Research
Lab research vision.
 Around 1,500-2,000 genes (~10%) are essential - necessary to live or for fitness. These represent a diverse set of biological functions, including metabolism, protein synthesis, transcription, the cytoskeleton, and more. Relative to their importance, there is still much unknown about these genes - including many that still have no known function!
Around 1,500-2,000 genes (~10%) are essential - necessary to live or for fitness. These represent a diverse set of biological functions, including metabolism, protein synthesis, transcription, the cytoskeleton, and more. Relative to their importance, there is still much unknown about these genes - including many that still have no known function!
Given their biological importance, mutations in essential genes often underlie rare diseases in humans. Some of these, such as Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation (CDGs), are so rare that any individual disorder can have less than 50 documented patients. Despite this, rare diseases collectively affect over 30 million in the U.S. alone, and there is a great need for new therapies for these diseases. Right now, our lab is focused on studying CDGs, but we are expanding into additional diseases soon.
A drug screen throughput.
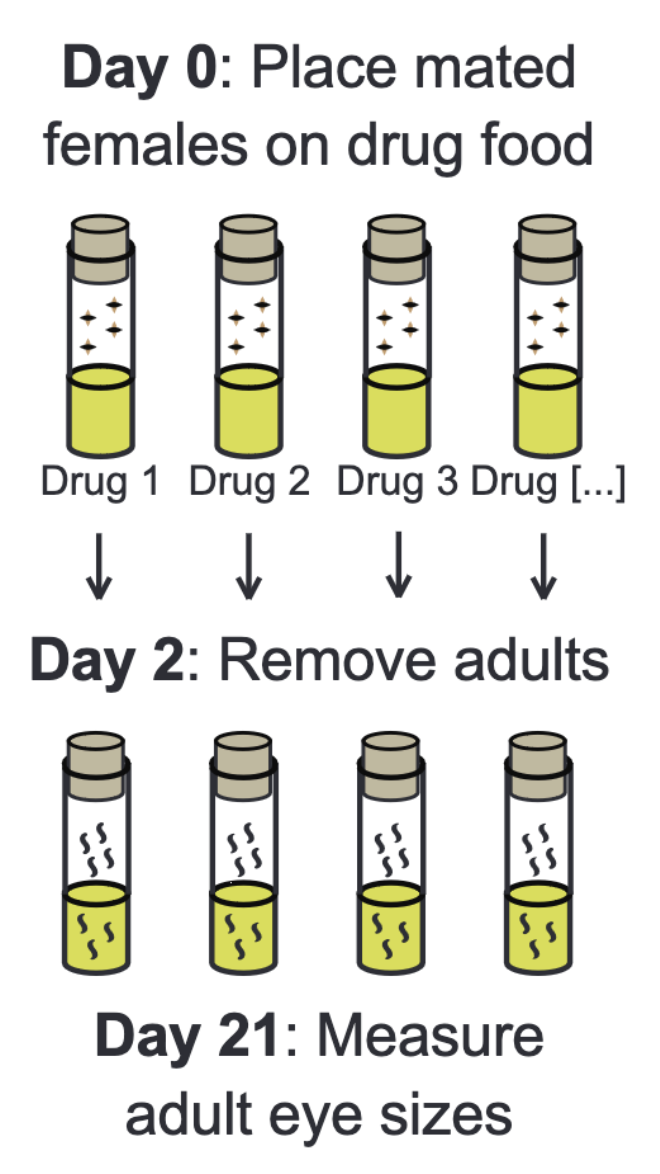 Our lab develops Drosophila models of a given disease that have strong, reproducible phenotypes. Using these models, we use a drug repurposing library of FDA-approved drugs to find drugs that can improve our disease models. The use of these libraries is critical, as they have the potential to accelerate future clinical trials.
Our lab develops Drosophila models of a given disease that have strong, reproducible phenotypes. Using these models, we use a drug repurposing library of FDA-approved drugs to find drugs that can improve our disease models. The use of these libraries is critical, as they have the potential to accelerate future clinical trials.
Validating top drugs. In the left example, this is an eye model of one of the diseases we study. You can see that drug feeding can have a strong effect on this phenotype! Top drug suppressors (because they “suppress” the phenotype) are validated by dose response in case certain concentrations are better or worse. We focus on the strongest drugs as well as those that have highly enriched mechanisms.
 One of the best properties of drug repurposing is that most of the drugs tested already have known mechanisms of action. This means we can also utilize the power of fruit fly and cell genetics to test the targets of these drugs directly through genetic manipulation. This is a powerful method to confirm our hit mechanisms! Because many of these genes are conserved (especially true of essential genes), these data are very relevant for humans regardless of whether a true new therapy is found. Interested? Here’s a paper on drug repurposing.
One of the best properties of drug repurposing is that most of the drugs tested already have known mechanisms of action. This means we can also utilize the power of fruit fly and cell genetics to test the targets of these drugs directly through genetic manipulation. This is a powerful method to confirm our hit mechanisms! Because many of these genes are conserved (especially true of essential genes), these data are very relevant for humans regardless of whether a true new therapy is found. Interested? Here’s a paper on drug repurposing.
Beyond drug screening. Essential genes are also fascinating from a basic science perspective. For example, in the context of aging biology, some essential genes can actually be beneficial to inhibit as an adult animal - increasing both healthspan and lifespan! The genomics of essential genes are also interesting - for example, why are there so many essential genes, when other similar genes have been duplicated? We are very interested in studying these questions and more!
